The selection between Turkey and the UAE for business establishment requires entrepreneurs to make a strategic decision about their operations. The UAE provides investors with a perfect environment for tax-efficient operations which attracts worldwide trade and digital service businesses. Turkey provides businesses with access to European and Asian markets through its strategic location and large domestic market. Your business needs either operational simplicity with tax benefits or market entry and manufacturing capabilities to determine your choice.
Choosing Your Global Business Hub: Turkey vs UAE
Entrepreneurs face their most important decision when selecting the country where they will establish their business operations. The Turkey vs UAE comparison presents two distinct investment opportunities which extend beyond geographical location. Your business model together with your industry requirements and long-term objectives will determine which economic system between Turkey and the UAE suits your company should choose. The following section explains all essential elements which will assist your decision-making process.

A visual comparison of Turkey and the UAE for entrepreneurs evaluating business setup advantages.
Core Economic Philosophies
The UAE established itself as a business-friendly environment through its smooth operations which Dubai and Abu Dhabi use to attract international investors. The free zones in the UAE attract worldwide investors through their complete foreign ownership benefits and tax-free status for eligible profits and their streamlined digital registration process. The following business sectors find the UAE an ideal location for their operations:
- International trade and logistics
- Technology and software development
- Financial services and consulting
- E-commerce and digital marketing
Turkey serves as a economic and political connection between European and Asian regions through its strategic position. The country maintains its economic strength through its diverse economy and large population of 85 million young people and its powerful industrial sector. The process of company establishment in Turkey requires traditional methods yet provides businesses with access to European and Central Asian and Middle Eastern markets. The country provides an ideal environment for businesses that want to establish production facilities or distribute products throughout regions or access a substantial consumer market. Our detailed guide provides additional information about Turkish investment opportunities for further exploration.
The UAE provides investors with a service-based economy that operates under low tax rates and maintains global business connections. Turkey operates as a production-oriented economy which enables businesses to access various regional markets through its integrated market system.
Your decision between Turkey and the UAE depends on which factors you consider more important between operational simplicity and tax benefits and market access and manufacturing capabilities. The following sections will provide detailed information about the specific procedures and expenses and legal framework and tax implications of each country.
Initial Comparison at a Glance
The following table presents a brief overview of the main differences between Turkish and UAE company formation procedures.
| Feature |
Turkey |
UAE (Free Zone) |
| Primary Advantage |
Strategic location, large domestic market, and a strong manufacturing base. |
Tax efficiency, ease of setup, and global connectivity. |
| Business Environment |
Dynamic and diverse, with a mix of traditional and modern sectors. |
Highly international, service-oriented, and structured around free zones. |
| Foreign Ownership |
Generally allows 100% foreign ownership, but some sectors have restrictions. |
Typically 100% foreign ownership with no local sponsor needed. |
| Taxation |
Standard corporate income tax and VAT system. |
0% corporate tax on qualifying income and no personal income tax. |
| Ideal For |
Manufacturing, regional trade, agriculture, and businesses targeting EMEA. |
International trading, tech start-ups, consulting, and service-based companies. |
The Company Formation Process Compared
The process of company establishment in Turkey and the UAE presents two opposing administrative approaches. The UAE operates as a digital-first platform which provides entrepreneurs with fast and efficient business setup procedures. The company formation process in Turkey follows established legal procedures which maintain a traditional approach to business setup. The initial step to understand your future workload and documentation requirements involves understanding these fundamental differences.The main distinction between Turkey and UAE company formation stems from their different approaches to bureaucratic procedures.

A side-by-side visual of UAE digital applications and Turkey’s document-based company registration workflow.
The UAE has developed an efficient process for business setup through its free zones which provide a smooth experience to entrepreneurs. The online platform enables you to complete most tasks from anywhere which reduces your time spent on location and minimizes your paperwork requirements.
The digital approach enables you to establish a UAE free zone company within a few days. The required documents for setup include ID and business plan without needing to obtain notarized copies of everything.
The UAE: Digital and Designed for Speed
The UAE provides investors with a quick path to establish their business operations through its mainland and free zone locations which number more than 40. The system operates at high speed which makes it attractive to investors who need immediate market access.
Here’s what that looks like in practice:
- Online Portals: Most authorities including free zones and mainland economic departments operate user-friendly online platforms which enable users to complete their applications and make payments through these systems.
- Minimal Paperwork: The document checklist is short. The application process requires you to submit your passport copies and business plan outline and complete the main application forms. The requirement for apostilled or notarised documents occurs less frequently than it does in Turkey.
- Rapid Registration: The time needed to obtain initial approval depends on your business location and activities but it usually takes 24 hours. The complete trade licence and incorporation certificate becomes available to you within a week after registration.
The UAE has implemented this method as part of its strategy to establish itself as a worldwide business center which enables companies to start operations without facing administrative delays so they can begin their business activities right away.
The UAE company formation process delivers both fast results and reliable outcomes to its users. The system operates to eliminate barriers which makes it suitable for international business owners who need to stay away from the entire setup process.
Turkey: A Formal and Structured Path
Turkey follows a different approach to company formation than the UAE. The process of company formation in Turkey requires entrepreneurs to work with established institutions while following a more direct path. The system provides complete security through its detailed process yet it requires investors to pay close attention to all its complex legal requirements. The systematic process guarantees complete adherence to Turkey’s complex and developed legal system.
The World Bank shows that Turkey operates 551 domestic companies through its stock exchange listings. The process of establishing a business in Turkey requires following a more complex procedure than what exists in the UAE. The process requires you to deposit minimum capital of TRY 10,000 for an LLC and complete notarization and register with the Turkish Trade Registry and local Chamber of Commerce. The process has become simpler but foreign investors must still follow all Turkish business laws. You can find more data about Turkey’s corporate activity on TradingEconomics.com.
The typical registration journey in Turkey breaks down into a few key stages:
- Draft and Notarise Documents: First, your company’s Articles of Association must be drafted in Turkish and then officially notarised. This is a non-negotiable step that requires professional legal help.
- Submit to the Trade Registry: With notarised documents in hand, you’ll submit everything—along with a potential tax ID and proof of your capital deposit—to the Turkish Trade Registry Office.
- Register with the Tax Office: Once the registry gives its approval, the next stop is the local tax office to officially activate your company’s tax identity.
- Register with the Chamber of Commerce: The final step is registering with the relevant Chamber of Commerce, which formally cements your company’s existence.
The longer registration process leads to establish a business in Turkey leads to obtaining a robust legal framework within a G20 nation. The process requires your physical presence or appointment of a legal representative for essential steps including notarization and bank account setup which increases your planning complexity.

Simplify your business setup with Workon’s all-in-one company registration service in Turkey.
A Realistic Look at Costs: Turkey vs. UAE
Your business decision between Turkey and UAE operations depends heavily on financial considerations. The setup fee from a price list does not represent the complete financial burden because you must calculate the minimum capital requirements and professional service expenses and annual operational costs. Your business will experience significant financial pressure before launch when you make incorrect financial decisions.
The financial requirements for business establishment differ substantially between Turkey and the UAE. The UAE business setup costs depend heavily on whether you choose mainland or free zone operations. Turkey provides a simple fee structure but demands shareholders to deposit share capital before registration.
Getting Your Company Registered: Initial Fees
The process of establishing a Limited Liability Company (LLC) in Turkey requires payment of specific fees which follow a predictable pattern. The process of registering your company requires you to pay for notary services to authenticate your Articles of Association and Turkish Trade Registry fees and Chamber of Commerce membership dues. The individual expenses remain small but they accumulate into substantial costs. The total expenses for company registration in Turkey will amount to $2,500 to $4,000 based on the level of professional assistance you require.
The UAE is a different story, with costs that can swing wildly depending on your choices:
- UAE Free Zones: You can find setups for as little as $3,000 for a simple service licence, especially in the northern emirates. But if you’re eyeing a prime free zone in Dubai, that number can easily climb past $15,000. This price usually covers your trade licence, registration, and often an initial visa allocation.
- UAE Mainland: A mainland setup is almost always the more expensive option upfront. You’re typically looking at a starting point of around $8,000, and that can go up quickly if your business activity needs special approvals from government ministries.
The Big Difference: Minimum Share Capital
The financial requirement for share capital stands out as the main financial distinction between these two locations. The business formation process requires you to provide legal funds which protect your creditors from financial risks.
The Turkish government demands all LLCs to maintain at least TRY 125,000 in share capital which equals $3,800 based on 2024 exchange rates. Your registration process requires you to place 25% of this amount into a business bank account before completion. The remaining amount needs to be paid within a two-year period.
Your business budget must include this essential capital contribution which Turkey demands for all new businesses. Your business needs actual funds for this requirement because UAE free zone setups typically require only paperwork-based capital verification. Your business startup liquidity will suffer from this requirement.
The UAE offers businesses complete freedom when it comes to minimum share capital requirements. Multiple UAE free zones operate without share capital requirements which benefits consultants and startups and service-based businesses that need minimal startup funds. The founding documents of mainland companies require capital statements but actual deposits are usually not required.
As you map out the capital you’ll need for your new business in either Turkey or the UAE, knowing how to secure that money is just as important. For a deep dive into your options, check out this ultimate guide to startup funding.
The following table presents estimated company setup and annual costs for Turkey and UAE operations.
Estimated Company Setup and Annual Costs Turkey vs UAE
The table presents standard LLC expenses for Turkish and UAE business operations. The costs presented in this table represent approximate values which might change depending on your business type and professional service providers and UAE free zone or emirate selection.
| Cost Component |
Turkey (Estimated USD) |
UAE (Free Zone, Estimated USD) |
UAE (Mainland, Estimated USD) |
| Initial Registration & Licence |
$1,500 – $2,500 |
$3,000 – $15,000+ |
$8,000 – $20,000+ |
| Professional Service Fees |
$1,000 – $1,500 |
Included or $1,500 – $4,000 |
$2,000 – $5,000 |
| Minimum Share Capital (Deposit) |
~$950 (25% of TRY 125k) |
$0 (in most cases) |
$0 (in most cases) |
| Annual Licence Renewal |
$1,000 – $2,000 |
$3,000 – $15,000+ |
$8,000 – $20,000+ |
| Basic Office Solution (Annual) |
$2,000+ (Co-working) |
$1,500+ (Flexi-desk) |
$5,000+ (Required Office) |
| Resident Visa (per person) |
N/A (Work Permit Process) |
$1,500 – $3,000 |
$1,500 – $3,000 |
The UAE operates through complete package deals in free zones yet Turkey operates through individual service selection with substantial initial investment needs.
What It Costs to Stay in Business Year-Round
Your business needs to maintain compliance and operational readiness through annual expenses that surpass initial setup fees.
The annual licence renewal fee in both countries requires substantial payment which approaches the initial setup cost. The operational expenses between the two countries show distinct patterns.
- Visa Costs: The UAE imposes substantial annual expenses for investor and employee visa requirements. The total cost for visa registration and medical testing and Emirates ID fees amounts to several thousand dollars for each person.
- Office Rent: The cost of commercial property rental in Dubai remains high. Free zone regulations require businesses to maintain office space even though they can use shared “flexi-desk” facilities. The process of locating affordable office space proves simpler in Turkey compared to other locations.
- Professional Help: Your business requires accountants and auditors to operate in both locations. The UAE requires businesses to undergo mandatory audits for specific company types. The UAE’s international business environment leads to higher costs for professional services which you need to pay.
A Tale of Two Tax Systems: UAE vs. Turkey
The tax environment of your business determines its long-term sustainability more than any other factor. The two countries operate under opposing tax systems because Turkey provides complete tax freedom to specific businesses yet the UAE implements traditional taxation with additional incentives.
The UAE maintains its position as a worldwide business center through its exceptional tax benefits. The government established this tax strategy to attract international investors and skilled workers. The UAE free zones offer businesses a 0% corporate tax rate for specific income streams.
The free zone environment attracts businesses that include international trading companies and tech startups and consultancies because they can operate within the zone without paying taxes. The absence of personal income tax in the UAE creates an ideal environment for hiring top talent because employees can retain their entire earnings.
The UAE: A Two-Track Tax Approach
The UAE maintains competitive tax rates for mainland businesses even though they need to operate outside free zones. The UAE government introduced corporate tax but implemented it as a soft policy which protects small businesses. The tax system operates with a basic structure that includes two tax brackets.
- Profits up to AED 375,000 (around $102,000) are taxed at 0%.
- Anything above that is taxed at a flat 9%.
The tax system protects new businesses and small and medium enterprises from excessive taxation during their initial growth period. The UAE has established itself as an investor-friendly destination through its digitalized processes which create a smooth experience for all users. The new corporate tax law brought transparency to the market by removing uncertainty which enables investors to create long-term plans. The UAE introduced complete foreign ownership rights for mainland businesses through major reforms which revolutionized the market. You can dig deeper into the key reasons investors are choosing the UAE on amca.ae.
The UAE’s offer is straightforward and potent: a potential 0% tax bill in a free zone or a low, predictable 9% on the mainland. This clarity is central to its appeal.
Turkey: A Strategy of Targeted Incentives
Turkey plays a different game. As a major G20 economy with a vast domestic market, it runs a more conventional tax system. The corporate income tax (CIT) rate has moved around a bit but typically sits between 20% and 25%. You’ll also deal with a standard Value Added Tax (VAT) system, usually at 1%, 10%, or 20%, depending on what you’re selling.
But just looking at those headline rates doesn’t tell the whole story. The Turkish government is very strategic, using a whole suite of financial incentives to attract investment into specific industries and regions. This creates fantastic opportunities where your real tax burden can drop dramatically.
Unlike the broad-brush approach of the UAE’s free zones, Turkey’s benefits are highly specific. Think of it less as a blanket discount and more as a series of special offers. These often include:
- Reduced Corporate Tax: If you’re based in a Technology Development Zone (Teknopark) or a designated industrial area, you could see your corporate tax rate slashed.
- VAT Exemptions: Buying certain types of machinery and equipment for your investment might be completely exempt from VAT.
- Social Security Support: The government might step in and cover the employer’s share of social security payments for a while, directly lowering your payroll costs.
- Customs Duty Exemption: Importing necessary machinery for a qualified project? You might not have to pay any customs duties.
What this means in practice is that if you’re a manufacturer, a research and development outfit, or an export-focused company, Turkey can be financially very attractive. The catch is that your business has to align with the government’s economic goals to unlock these perks. It’s a sharp contrast to the UAE, where the benefits are much more universal and less tied to your specific sector.
The infographic below really hammers home one of the most critical decision points: taxes.
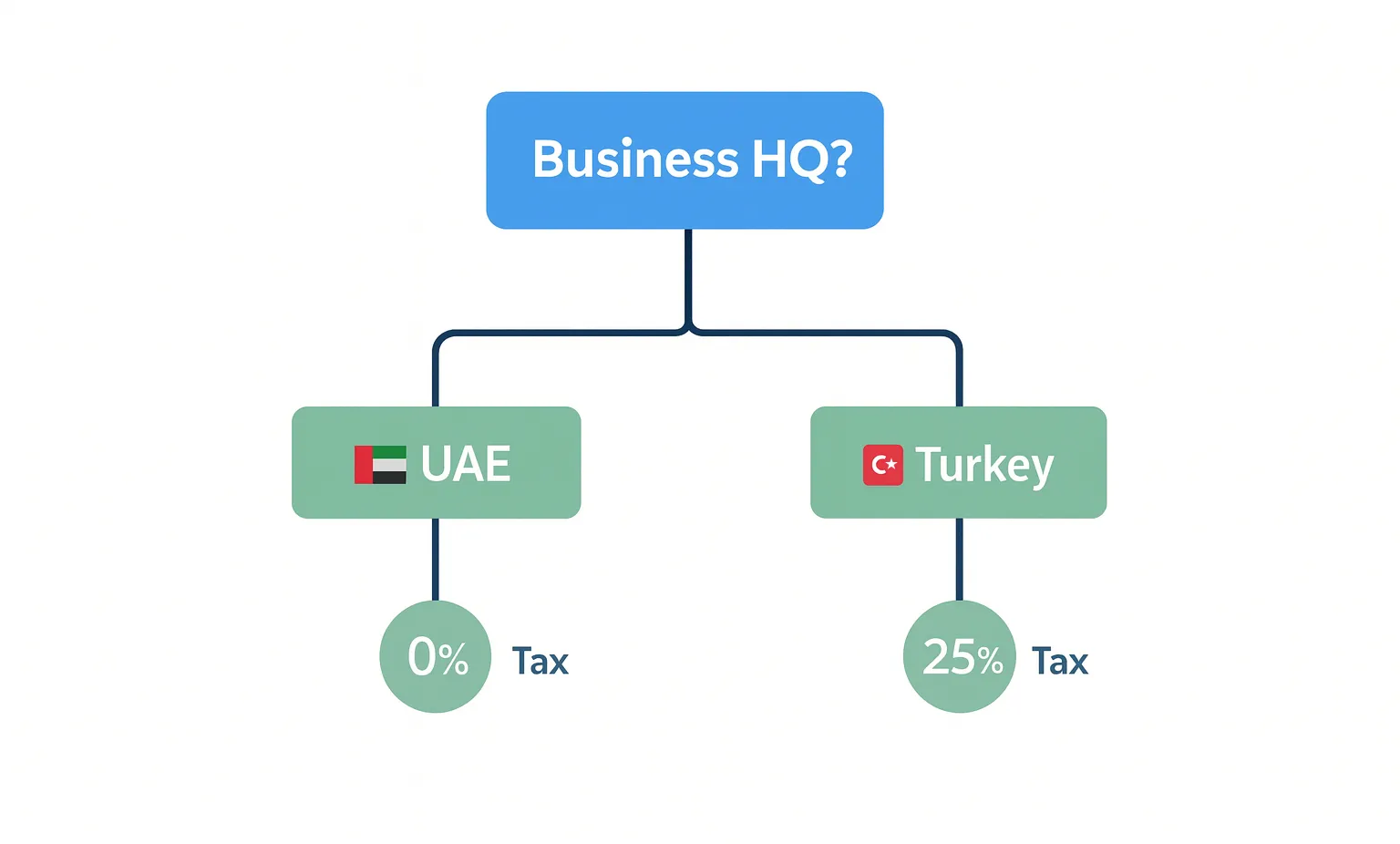
UAE vs. Turkey Corporate Tax Rates for Business Headquarters
This visual shows the stark contrast in tax burdens, a make-or-break factor for most service-based and digital companies.
Which Country Best Fits Your Business Model
The selection between Turkey and the UAE depends on which nation offers better strategic alignment with your business operations. Your business model determines which country will provide the most beneficial strategic alignment. Your business success depends on your industry sector and customer base and operational structure and long-term business targets.
A business strategy that succeeds for one organization will fail for another organization. We will analyze actual business cases instead of discussing general advantages and disadvantages between Turkey and the UAE. The comparison between Turkey and the UAE for company formation will become clearer through examples that demonstrate how each country’s unique benefits match various business operations.
E-commerce and Digital Services
For anyone in e-commerce, digital marketing, or online consulting, the UAE usually makes a much stronger argument. The big draws are its tax system and incredibly smooth administrative process. Setting up in a UAE free zone means you can qualify for 0% corporate and personal income tax, which directly boosts your bottom line.
This is a huge advantage for businesses that don’t need a lot of physical space and serve customers worldwide. You can often register a company entirely online, operate with minimal red tape, and focus your energy on growing the business instead of wrestling with local regulations.
Tech Startups and Venture Capital
The UAE attracts most tech startups that seek venture capital and fast expansion because of its location in Dubai. The entire system in Dubai exists to support innovation through direct access to international funding sources and business accelerators and a large pool of global professionals who receive tax-free compensation.
The UAE free zones operate with fast scalability and high operational speed. The UAE provides tech startups with superior infrastructure when they want to launch their business quickly and connect with international funding sources.
Turkish tech startups that create solutions for domestic manufacturing and agricultural industries will discover better support within their home market. The Teknoparks in Turkey provide substantial tax reductions and research and development funding to support innovation that serves the national industrial base.
Manufacturing and Physical Production
Turkey stands as a leading manufacturing destination because it specializes in producing physical products. The European Union market remains accessible to Turkish businesses through their Customs Union agreement which provides tariff-free entry. The location of Turkey provides businesses with excellent market access to European Union markets and Middle Eastern and North African and Central Asian markets. The location of Turkey creates an ideal situation for manufacturers because it provides them with excellent market access to multiple regions.
Turkey maintains a developed industrial sector and trained workforce and lower operational expenses for utilities and labor costs compared to the UAE. The government provides financial support to businesses operating in specific industrial zones which reduces their initial costs and ongoing expenses. The manufacturing sector of Turkey operates as a perfect environment for businesses that produce machinery and textiles and automotive components.
International Trading and Logistics
The selection of trading location depends on the specific products you handle and their intended destinations.
- For high-volume, global re-export: The UAE is almost always the winner here. With world-class ports like Jebel Ali and free zones built for logistics, it’s an incredibly efficient hub. The lack of customs duties within these zones and simplified import-export rules make it perfect for managing global trade flows.
- For trade linked to regional production: If your business deals in goods made in or destined for Europe and its neighbours, a Turkish base makes more sense. You get direct access to production lines and robust land-based logistics networks that stretch right into the EU, giving you a clear operational advantage.
Ultimately, the best decision comes from a hard look at your own business. You need to align your model with the core strengths of each country—the UAE’s tax efficiency and status as a global service hub versus Turkey’s industrial depth and unmatched regional market access.
So, Where Should You Set Up Shop? A Final Look
The selection between Turkey and the UAE depends on which country matches your business requirements better. The selection between Turkey and the UAE depends on which country matches your business requirements better. The decision between Turkey and the UAE for company formation depends on strategic alignment rather than which country is superior.
Your business direction should determine which location you choose for establishment. The UAE has developed an extensive business framework which delivers fast operations and simple administrative procedures and complete tax exemption. The UAE provides an exceptional environment for businesses that operate worldwide because it minimizes their tax responsibilities.
The UAE is probably your best bet if you’re running:
- A tech startup or software firm looking to attract international investment.
- A global trading or logistics company coordinating complex supply chains.
- A service business, like a consultancy or digital agency, that serves clients all over the world.
Finding the Right Home for Your Business
Turkey offers distinct business advantages which make it an equally strong option for companies. The country benefits from its excellent geographical position and established industrial sector and substantial local market demand for new business offerings. The strategic position of Turkey between Europe and Asia makes it an ideal location for businesses that deal with physical products and regional trade operations.
Turkey should be at the top of your list if your business is focused on:
- Manufacturing or assembly, especially if you plan to export to the EU and neighbouring markets.
- Regional distribution, taking advantage of Turkey’s advanced logistics infrastructure.
- Selling directly to a large and dynamic domestic consumer base.
The bottom line is simple. If you need a tax-light, globally-connected hub for a service or trading company, the UAE is the clear choice. If you’re building a business centred on manufacturing or regional market access, Turkey offers a launchpad like no other.
By honestly weighing these fundamental differences against what your business truly needs, you can make a confident choice. Think of your business plan as the map—these two countries are just different destinations, and your job is to pick the one that gets you where you want to go.
Frequently Asked Questions
Thinking about setting up a business in Turkey or the UAE? You’re not alone, and it’s normal to have a few questions. Let’s tackle some of the most common ones that come up when you’re weighing your options.
Can I Get Residency by Setting Up a Company in Turkey or the UAE?
Absolutely. In both countries, starting a business is a well-trodden path to residency. In the UAE, forming a company is one of the most direct ways to get an investor or employment visa for you and your family. If you’re planning a more significant investment, you could even qualify for their long-term Golden Visa programme.
Turkey offers a similar route. As a business owner, you’re eligible to apply for a residence permit. Plus, for those looking to plant deeper roots, making a substantial investment—like buying property or creating local jobs—can open a clear pathway to Turkish citizenship over time.
Which Country Is Better for a Small Online Business?
For most small online businesses, solo entrepreneurs, or digital nomads, the UAE often has the edge. The country’s whole free zone system feels like it was practically designed for this kind of operation.
It’s the combination of benefits that makes it so appealing for service-based digital companies:
- The setup costs are generally very low, and you can handle most of the registration online.
- You can potentially benefit from 0% corporate and personal tax on your income.
- You get guaranteed 100% foreign ownership from day one, no questions asked.
What Are the Main Banking Challenges in Each Country?
Opening a corporate bank account is a hurdle you’ll face in both places, but the challenges are different. The UAE’s banking system is world-class and deeply integrated into the global economy. The catch? The due diligence process can be incredibly thorough and slow, and most banks will expect you to maintain a hefty minimum balance.
In Turkey, you might get an account opened faster, assuming your paperwork is flawless. The main difficulties tend to surface later. You’ll need to get comfortable with local banking regulations and be prepared for the realities of currency volatility, which can directly impact your capital.
While both countries have modern banking, be ready for a meticulous due diligence process in the UAE. In Turkey, the bigger concern is staying ahead of economic factors like currency fluctuations.
Is 100% Foreign Ownership Possible in Both Countries?
Yes, but how you get there differs. In the UAE, 100% foreign ownership is the norm in its many free zones. It has also become widely available for most business activities on the mainland, which is a significant recent change.
Turkey also allows 100% foreign ownership across most sectors. However, if your business falls into a strategic industry like energy or media, you might run into specific restrictions or need extra government approvals. This can make the process a bit more involved compared to the more straightforward structure in the UAE.
Ready to navigate the company formation process in Turkey with expert guidance? Workon specialises in simplifying every step, from registration and banking to residency permits, ensuring your business is built on a solid foundation. Start your journey in Turkey with Workon today.
The UAE is better for fast digital setup and tax benefits, while Turkey is ideal for manufacturing, regional trade, and accessing the EU, MENA, and Central Asian markets.
The UAE offers 0% corporate tax in most free zones and a 9% corporate tax on mainland profits. Turkey applies 20–25% corporate tax but offers targeted tax incentives in industrial and technology zones.
The UAE offers a nearly fully digital process that can be completed within days. Turkey requires notarisation, trade registry approval, and in-person steps, making the process longer.
Turkey requires a minimum share capital of TRY 125,000 for LLCs, with 25% deposited upfront. Most UAE free zones do not require depositing actual capital.
Yes. The UAE permits 100% foreign ownership in free zones and most mainland activities. Turkey also allows full foreign ownership, except in a few regulated sectors.